Basic Computer
Inside a computer: This is how your pc is built
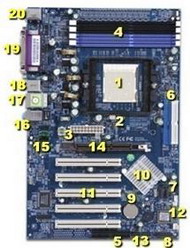
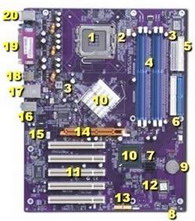
1. CPU Socket (for processor)
2. CPU fan connector
3. ATX power supply connector (for plug from power supply in computer case)
4. Memory Slots (for memory modules- new mainboards use DDR, previous generation uses SDRAM)
5. Floppy Drive Connector (for data cable to floppy drive)
6. Primary & Secondary IDE Connectors (data cable for hard drive, CD drive - up to two devices per connector)
7. Serial ATA Hard Drive Connectors (1 drive per connector)
8. Panel for connecting power switch, reset switch, hard drive light, etc.
9. CMOS Battery (keeps current BIOS Setup information intact)
10. Chipset (controls specific functions)
11. PCI Slots (for plugin cards such as modems, network cards, PCI video cards, sound cards, etc.)
12. BIOS chip (see explanation below)
13. USB Headers (for additional USB ports)
14. AGP Slot (for Accelerated Graphics Port video card, today's standard)
15. Connector for CDROM audio cable (for sound already built onto mainboard)
16. On-board Audio Jacks (line in, line out, microphone jacks)
17. LAN Jack (for onboard Ethernet Controller)
18. USB 2.0 Ports
19. Parallel Port & Serial Ports (parallel printer port plus one or two serial ports which are hidden from view)
20. Keyboard & Mouse Connectors (PS2 connectors, one for keyboard, one for mouse) Many mainstream PC's today, especially lower priced ones, have the AGP Video controller, the Audio controller, Modem and NIC (Network Interface Card) built onto the mainboard rather than on separate plug-in cards. On-board video uses a portion of the memory provided by the plug-in memory modules which is typically reserved for the rest of the system. This type of video does not perform well when used for high-end graphics such as games. It is possible that, even though the video chip is built on board, the manufacturer may have supplied an AGP slot so you can install your own Video card. Today's video cards contain at least 32mb of their own memory, and may go up to as high as 256mb. The on-board video would first need to be disabled in the BIOS/CMOS setup routine before installing the card. If the modem, sound, or network interface fail, or you want to upgrade them, they can usually be disabled in the BIOS settings also, allowing for installation of a plug-in replacement card.